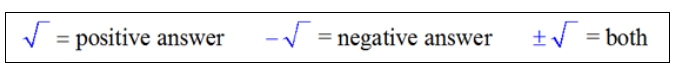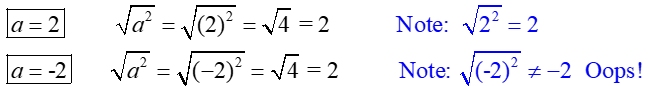of "root" is determined by the appearance of the "index" value.
Positive and/or Negative Square Root Values? |
|
 |

Remember, there is an
accepted rule (referred to as the "
Principal Square Root") about evaluating square roots (or any radical with an
even index). This accepted rule states that the
evaluation will ALWAYS yield a positive value (or 0). If a negative value is wanted, the square root must carry a negative sign in front of the radical symbol.
The purpose of this rule is to avoid confusion. When there are two possible solutions to a square root, how do you know which one is needed in a specific problem? This accepted rule specifies that there is only ONE recognized answer for the solution to a "naked" square root (one without a + or - in front of the radical symbol). This rule avoids any possible confusion.
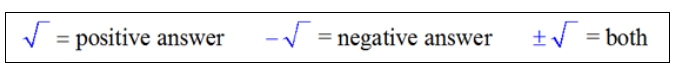 Note: "positive", as stated above, is technically "non-negative" if we consider the possibility of "0".
Note: "positive", as stated above, is technically "non-negative" if we consider the possibility of "0".
Remember:

Only a negative sign in front of a square root symbol can indicate a negative solution. Otherwise, the square root symbol alone yields a positive solution only. |
Note: This situation does not exist with odd index problems, since there is only one possible solution for a radical with an odd index. No confusion.
Consider:
You have seen a square root associated with both "positive" and "negative" values in the solution of a quadratic equation, such as x2 = 36. This equation is solved by taking the square root of both sides of the equation. Since this quadratic equation has two possible solutions, both the positive and negative values of the square root are correct solutions.
Thus, we write: 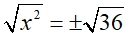 (there MUST BE the plus/minus sign out front).
(there MUST BE the plus/minus sign out front).
The solution to the equation is x = ± 6, since both (6)2 and (-6)2 give 36.
(If we did not write the ± symbol, the only solution to the equation would be x = 6.)
This is why your teacher was so insistent that you include that ± symbol in your answer:
because without the ± symbol, your answer was technically incorrect.
It may seem logical to think that
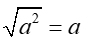
, but this is not necessarily true.
Consider what happens when
a = 2 and when
a = -2.
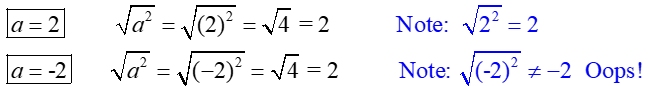
The "Oops" is pointing out the fact that taking the square root of a perfect square, will return the value being squared.
Example: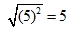 . But. the square root of (-2)2 = the square root of (4), which is +2 (not -2)
. But. the square root of (-2)2 = the square root of (4), which is +2 (not -2)
Remember, for a square root to give a negative result, it must have a negative sign in front of the radical symbol.
The following mathematical statement avoids this "Oops!" problem:
The square root of a2 is always a positive real number for any non-zero real number a.
Since absolute value also always yields a positive real number
for any non-zero real number a, we can say that :
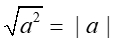 for any real number a.
for any real number a.
Which indicates that the principal square root of a2 is the absolute value of a.
To avoid any possible mathematical inconsistencies, you will see directions given, such as:
"Assume all variables represent positive values and the radicand is non-negative."
If such "directions" are NOT given, then technically the absolute value symbol
must be used when simplifying: 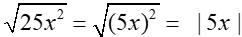 .
.
 This problem only pertains to square (and other even) roots.
This problem only pertains to square (and other even) roots.
There is no need to use the absolute value signs when the index is odd.
Where does a square root (or any radical) fall in the "order of operations" (PEMDAS)?
Working with roots is essentially considered, in the order, under "exponents".
(Which we will discover, is a logical placement, considering the relationship between radicals and exponents.)
Radicals (roots) are evaluated after Parentheses, and before Multiplication and Division.
If there is an expression under the radical (the radicand), that expression is considered as being in a set of parentheses,
which is evaluated before the radical root is applied.
In PEMDAS, we consider E = exponents (powers and roots).
The term "surd" refers to a number left in radical form for accuracy, which when written in decimal form would go on forever without repeating. The number under the root symbol is a rational number and is not a perfect square. Surds are roots that are irrational numbers, with the most common reference being to "quadratic surds".
Surds which have a root index of two are quadratic surds.
Surds which have a root index of three are cubic surds.
Surds which have a root index of four are fourth order surds.
And so on ... |
|